
NIR-II Imaging
Micro-Lens Array (MLA)
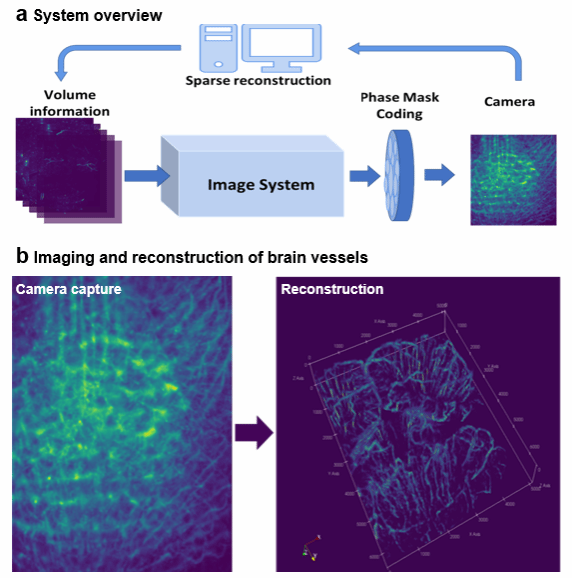
Conventional microscopes rely on stepwisescanning to record three dimensional (3D) information, and havelimited penetration depth due to strong scattering of visible light.We introduce a non-scanning 3Dmicroscope, reconstructing cortex-wide volume from a singletwo-dimensional (2D) measurement, enabling fast recording of volumetricdynamics in a large depth range.Basic thoughts:
• Encoding signals from different depth and reconstructing the wholevolume.
• Imaging in the near-infrared II (NIR-II,1000~1700nm) spectralfor larger penetration depth that covers all cortex layers.
Metasurfaces
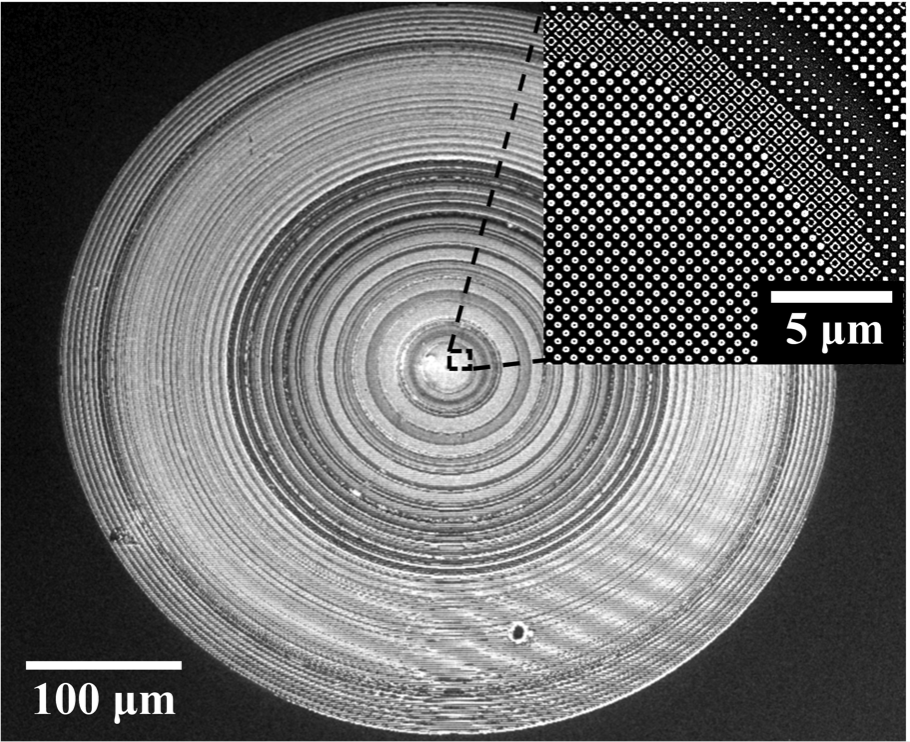
Metalens, a two-dimensional metasurfacestructure, has gained much attention in the recent years. With ultra-thin andultra-lightweight structural properties, metalens offers precise and flexibledesign to control the wavefront. In imaging field, metalens provides amulti-dimensional perspective for exploration.
Structured Illumination Imaging
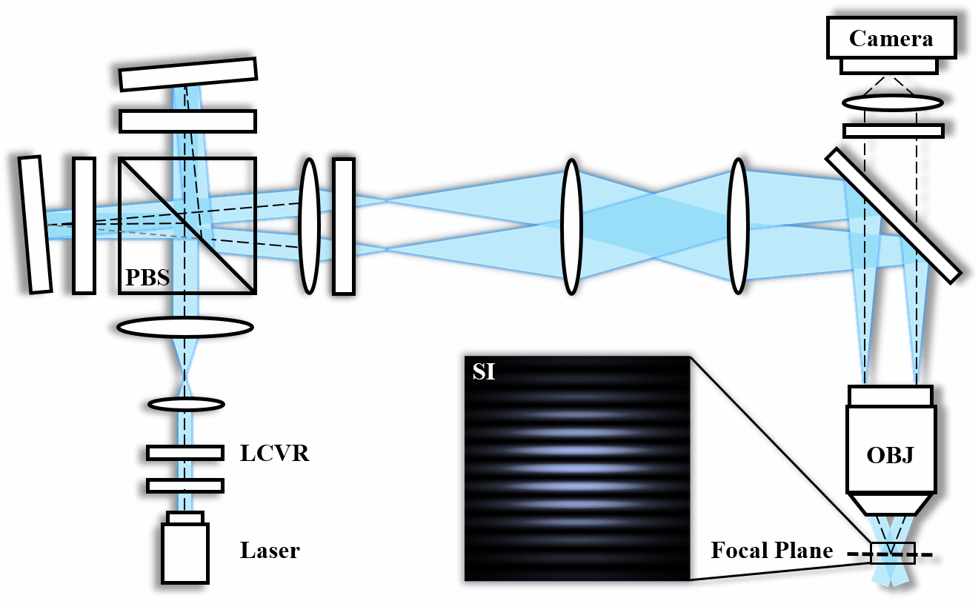
Traditional wide-field fluorescence microscopes capture both in-focus structures and out-of-focus background, lacking the capability for optical sectioning. By using a periodically varying structured light pattern to illuminate the specimen, Optical Sectioning Structured Illumination Microscopy (OS-SIM) can obtain three-dimensional structural information while retaining the advantages of a wide-field microscope. In combination with the near-infrared window, the proposed NIR OS-SIM system enables in vivo 3-D cerebrovascular imaging with a large imaging depth, offering new insights for brain science research.
Pre-Clinical Imaging
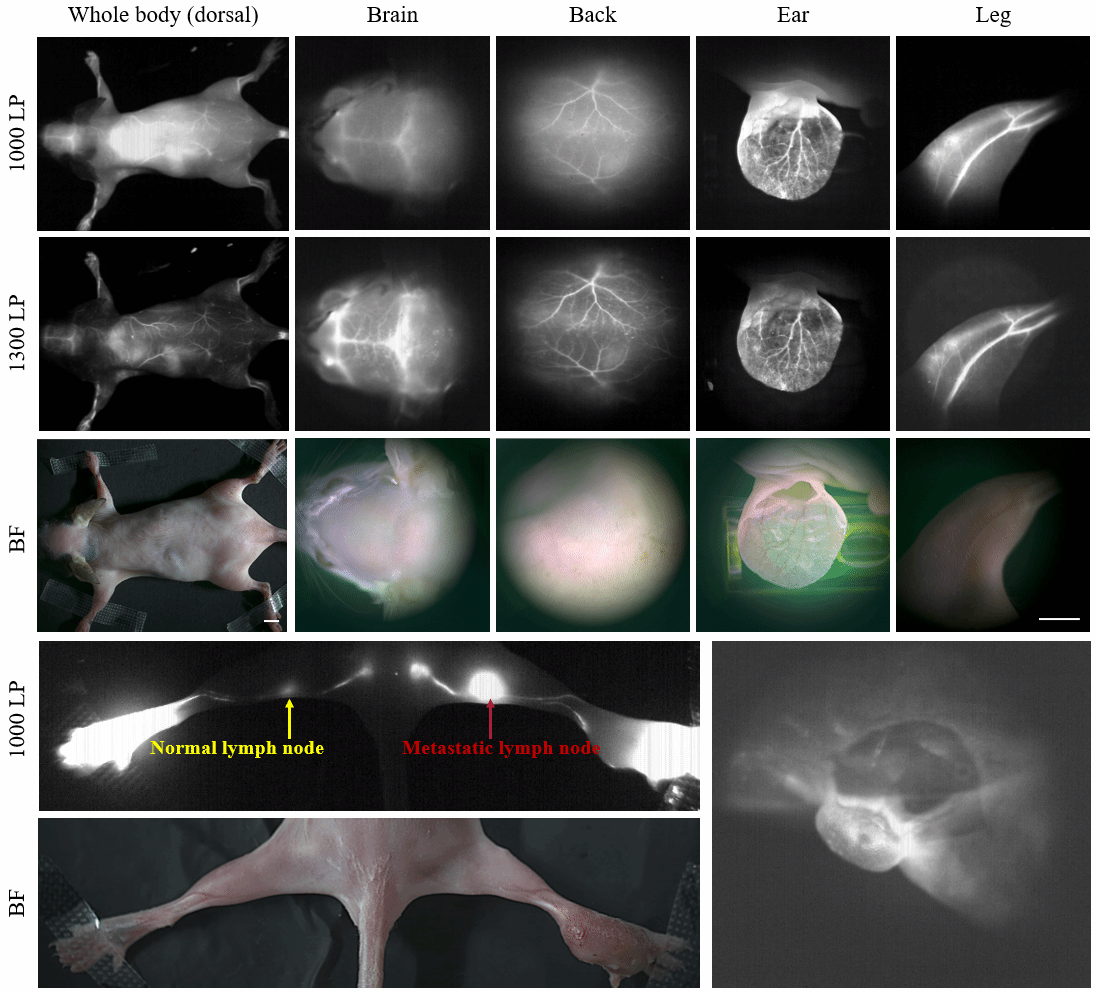
We designed and built amacro/micro dual-channel imaging system based on visible and NIR II, which canachieve imaging of both large and small fields of view by switching objectivelenses. The system resolution and signal background ratio were tested andcharacterized by angiography of the whole body of mice. The imaging system canimage the blood vessels of mice all over the body at one time and can switchthe small field of view to observe the area of interest at higher resolution.With the aid of the surgical navigation system, the surgeon can accuratelyremove the tumor, detect the sentinel lymph node and judge its metastasisstatus during the operation.